Which Programming Languages and Frameworks Will You Hear About as a UX Designer?
With hundreds of programming languages, it can be overwhelming for UX and product designers to comprehend or decide which one is worth learning. While learning code isn’t essential for a UX designer’s job, it can help them understand technical constraints and improve collaboration with development teams.
This article explores six programming languages for UI/UX designers and why coders use one over the other. We also explain the difference between programming languages, front-end frameworks, and component libraries and how they influence design projects.
Our proprietary Merge technology will take your design projects to the next level with component-driven prototyping in UXPin. Visit our Merge page for more details and how to access this revolutionary UX technology.
What are Programming Languages?
Programming languages are the code developers use to write websites, algorithms, and digital products. Each programming language has its own markup, rules, structure, package manager, etc.
There are hundreds of programming languages, most of which product teams will never encounter. We’ve narrowed down a list of essential coding languages, so you know where to start if you wish to research these further.
How do Programming Languages Impact the Product Development Process?
A programming language dictates the product’s technical constraints, significantly impacting product development, including the user experience design process.
Design teams must understand these limitations or risk wasting time designing solutions and features that programmers can’t build.
The programming language also influences other product development decisions which ultimately impact UX, for example:
- Time-to-market
- Back-end technical infrastructure (impacts budgets and performance)
- Engineering talent (human resource availability and cost)
- Functionality/scalability through APIs and integrations
Programming Languages vs. Front-End Frameworks
It’s important to distinguish a programming language from a front-end framework. For example, Javascript is a programming language, while React, Angular, and Vue are all Javascript frameworks.
Frameworks are built using programming languages, offering software engineers automation, tools, libraries, functionality, templates, session management, etc., to develop websites and applications more efficiently than coding from scratch.
What is a Component Library?
Component libraries add another layer of confusion for people with a limited code skill set.
Component libraries are code components of a design system featuring ready-made UI elements engineers use to build user interfaces. A popular example is MUI, a React component library built on Google’s Material Design UI.
The designer’s equivalent of a component library is a UI kit that features vector-based graphic elements used in design tools. If you’re still confused, this article explains the difference between design systems, pattern libraries, style guides, and component libraries.
Which Programming Languages Will UX Designers Encounter?
This is a tricky question to answer because designers are more likely to encounter front-end frameworks (usually Javascript-based) and component libraries rather than the individual programming languages behind them–which, as we have learned, are entirely different things.
For this reason, we’ve created two categories:
- Programming languages
- Front-end frameworks
Programming Languages
Here are six programming languages UX designers will most likely encounter during their careers.
1. HTML
HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language and is the markup used in web browsers. It’s the foundational language every engineer must learn to build websites and web apps. Whether you use a front-end framework or not, a web browser will always render HTML, along with some CSS and Javascript for styling and interactivity.
Learning basic HTML as a UX designer is never a bad idea, as this will give you a foundational understanding of front-end coding.
2. CSS
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a style sheet language used to style content with color, layouts, fonts, etc. Without CSS, every website would look identical, featuring the basic styling properties rendered by HTML.
CSS is another essential language for user interface designers because it’s relatively simple to comprehend and significantly impacts UI design.
3. Javascript
Javascript is another core internet language for websites and web applications. Its primary role in web development is providing interactivity and functionality alongside HTML and CSS.
Javascript is also widely used for many front-end frameworks, including React, Vue, Ember, and Angular, to name a few. Companies use these frameworks to build many of the web and mobile apps we use every day.
4. Java
Not to be confused with Javascript, Java is a programming language maintained by software giant Oracle, primarily used to build enterprise applications. Java also powers many hardware devices like smartwatches, fridges, SmartTVs, and wearables, to name a few.
5. PHP
PHP is most well known as the programming language behind the popular content management system, WordPress. It was also the original language behind early Facebook before the social media giant developed React, which now powers most of Meta.
6. Python
Python is another popular front-end programming language used by Meta for Instagram. The language is also popular for artificial intelligence and machine learning applications due to its lean code and pre-built algorithm libraries.
What are the best language for web design?
Here’s a straightforward stack that will come in handy for web design.
- HTML (Hypertext Markup Language): HTML will provide the structure of your website, including sections for displaying information about your company, products/services, and a sign-up form.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): CSS will be used to style your HTML elements, making your website visually appealing and cohesive.
- JavaScript: Use JavaScript for client-side validation of the sign-up form to ensure that users enter valid email addresses and any other required information. You can also use JavaScript to enhance user experience with features like smooth scrolling, interactive animations, or displaying notifications.
- PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) or Node.js: For the backend functionality of collecting and storing sign-up information, you can use either PHP or Node.js. PHP is straightforward and commonly used for handling form submissions, interacting with databases, and sending emails. Node.js, on the other hand, can provide a more modern and scalable backend solution.
- SQL (Structured Query Language): Use SQL to interact with a database where you’ll store the collected sign-up information.
With this stack, you can create a simple and functional company website that collects emails and sign-ups effectively. You can start by designing the layout and styling using HTML and CSS, then implement client-side validation and interactivity with JavaScript, and finally, set up the backend functionality for collecting and storing sign-up data using PHP or Node.js and a database with SQL.
What are Front-End Frameworks?
For this article, we’ll focus on four Javascript frameworks commonly used for web and mobile applications.
These frameworks are also compatible with UXPin Merge–a technology that enables designers to use ready-made UI components from a design system to build fully functioning prototypes. Check out our Merge page for more details.
1. React
React is a popular Javascript framework for developing web and mobile applications (iOS and Android)–although organizations typically use React Native for the latter. The component-based markup and flexibility to create cross-platform applications make React a popular choice for product development worldwide.
2. Ember
Ember is a Javascript framework for building web applications. Many popular apps use Ember, including Netflix, Square, LinkedIn, and Twitch, to name a few.
3. Angular
Developed and maintained by Google, Angular is a popular framework for building cross-platform applications. PayPal, GMail, Upwork, and the Forbes website are just a few platforms that use the front-end framework. Angular’s out-of-the-box interactivity and functionality make this framework popular for complex applications.
4. Vue
Vue is a Javascript framework for building single-page web applications. Vue allows you to encompass HTML, making it an easy framework to learn for people with HTML, CSS, and Javascript coding skills. The framework also offers excellent performance and a comprehensive ecosystem to scale applications.
What are the Benefits of Using Programming Languages?
Using programming languages during the design and prototyping process is not uncommon. Designers can create live-data prototypes with code, accurately replicating the final product user experience.
These code prototypes allow designers to test features with the same fidelity and functionality as the final product, thus delivering better quality results and feedback.
The problem with using code for prototyping and testing is it adds time to the design process and requires the skills of a front-end developer or UX engineer–valuable resources that increase the project’s costs.
For this reason, organizations reserve code prototyping for solving complex usability issues and typically build a single screen or user flow to save resources.
UXPin Merge – A Design Tool That Renders Code
With a code-based design tool like UXPin Merge, designers can achieve the same results without writing a single line of code. Merge allows design teams to sync a design system from a repository to UXPin’s editor, so designers and engineers use the same UI elements during the design and development process.
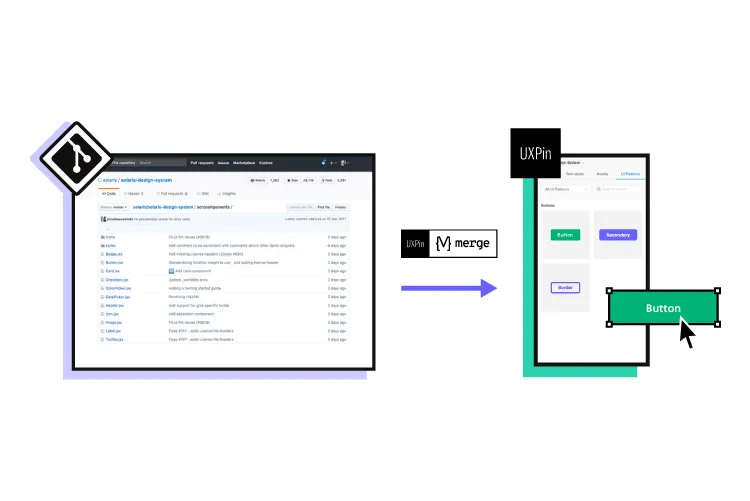
Merge works with many popular front-end frameworks, including React, Vue, Ember, Angular, and more. Designers use these components in any other design tool, but they come ready-made with states, animations, and properties defined by the design system.
Faster Prototyping, Better Collaboration
Component-driven prototyping is significantly faster than image-based design because designers only focus on building UIs rather than designing UI elements from scratch.
This single source of truth improves designer/developer collaboration because everyone speaks the same language and works within the same constraints. Design handoffs in Merge are seamless, almost non-existent because engineers have the same component library–it’s just a matter of matching the designs from UXPin.
Scalable
Merge makes it easy to scale and mature a component library with Patterns. Designers can combine multiple elements to build new UI components and patterns. If their design system doesn’t have what they need, designers can use UXPin’s npm integration to import components from open-source libraries to build new patterns.
Enhanced Testing
Merge allows design teams to create immersive, dynamic prototypes that accurately replicate the final product experience, resulting in meaningful feedback from user testing and stakeholders.
Design teams can send stakeholders a link to the prototype and receive actionable feedback via UXPin’s Comments feature. Stakeholders can even assign comments to specific team members.
“Our stakeholders are able to provide feedback pretty quickly using UXPin. We can send them a link to play with the prototype in their own time, and UXPin allows them to provide comments directly on the prototypes.” Erica Rider, Senior Manager for UX – Developer tools and platform experience at PayPal.
With UXPin Merge, design teams don’t need to learn a programming language or collaborate with engineers during prototyping to achieve the benefits of code. Visit the UXPin Merge page to learn more about this revolutionary technology and how it can improve your end-to-end product development process.